Ground water Recharge Systems in Delhi: A Sustainable Solution for Long-Term Water Security
India depends heavily on groundwater for drinking, agriculture, and daily life. But with rising population, over-extraction, and changing climate patterns, groundwater levels are falling fast especially in urban regions like Delhi. A well-designed Ground Water Recharge System helps reverse this damage by allowing rainwater to return to the earth, where it belongs.
These systems are not just technical solutions. They are long-term investments in water security, resilience, and sustainability.
Why Ground Water Recharge System Is Essential Today
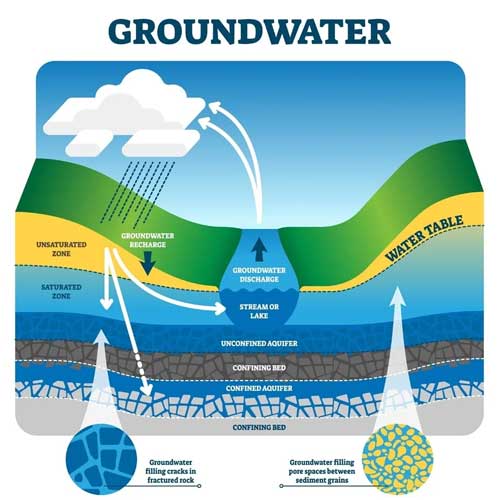
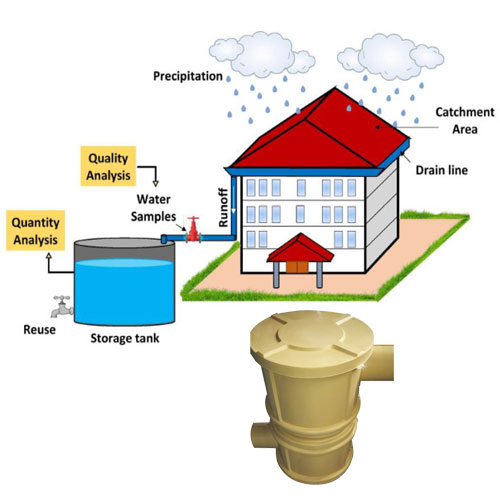
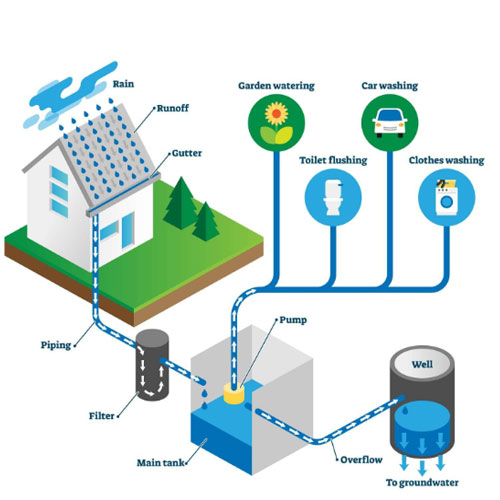
A Ground Water Recharge System works by guiding rainwater and surface runoff into underground aquifers. Instead of letting rainwater flow away into drains, the system helps it seep slowly into the soil, just like nature intended.
The benefits go beyond refilling groundwater levels:
-
Restores declining water tables
-
Improves groundwater quality
-
Reduces flooding and surface runoff
-
Builds long-term water availability for communities
In water-stressed cities, recharge systems are no longer optional, they are essential.
Ground Water Recharge System in India: Adapting to Diverse Conditions
Rainfall patterns across India vary widely. This makes it important to design Ground Water Recharge Systems in Delhi that are customized to local soil, land use, and climate conditions.
Different regions require different recharge methods, what works in rural catchment areas may not work in dense urban spaces. That’s why a flexible and location-specific approach is key.
Common Types of Ground Water Recharge Systems
Percolation Tanks & Check Dams
These structures are built in areas where surface runoff is high, such as foothills or natural drainage paths. They slow down rainwater flow and allow it to gradually percolate into the ground.
Along with groundwater recharge, they also help:
-
Control floods
-
Prevent soil erosion
-
Store water for dry periods
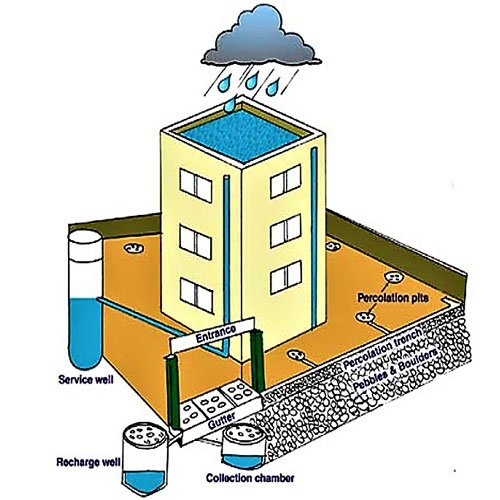
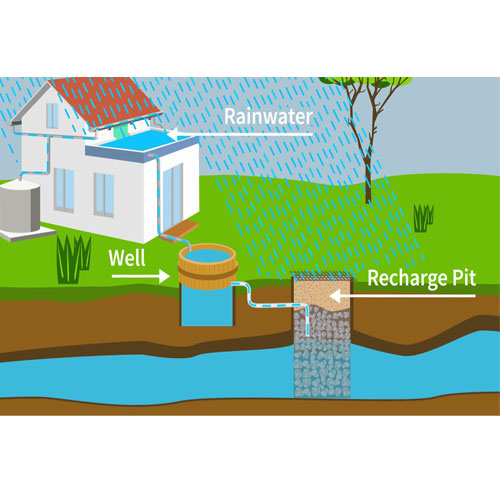
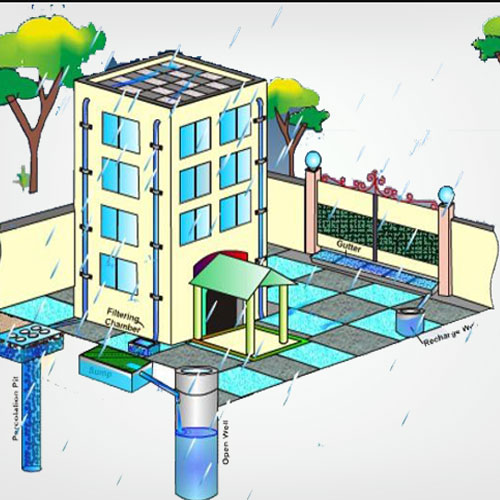
Recharge Wells and Borewells
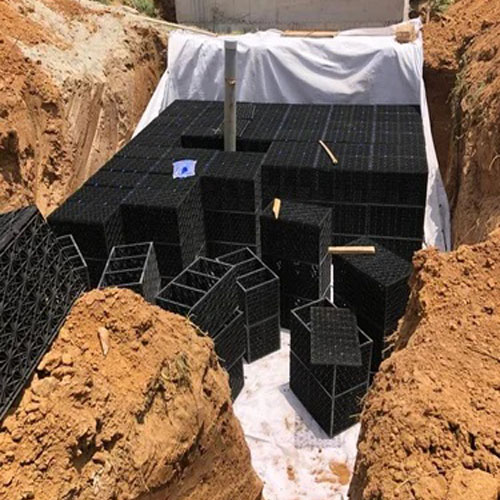
Recharge wells allow rainwater to directly enter underground aquifers. Fitted with filters and permeable layers, these wells are especially effective in cities where open land is limited.
They are commonly installed in:
-
Residential societies
-
Parks and campuses
-
Commercial and public buildings
This makes them a practical Water Recharge System for urban groundwater restoration.
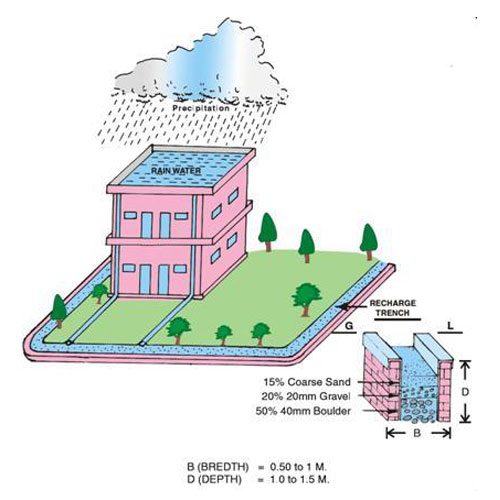
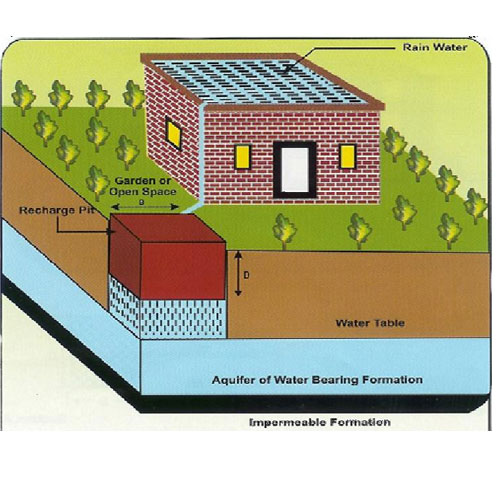
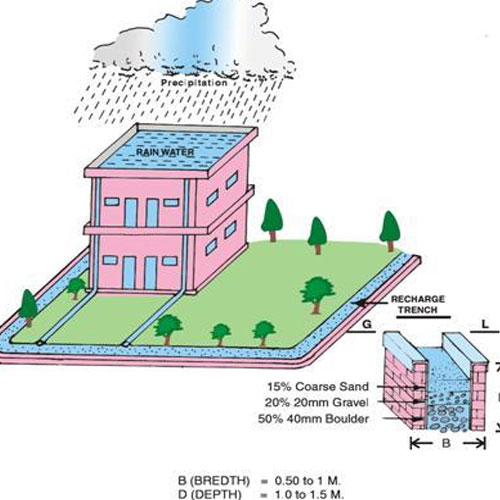
Recharge Pits and Trenches
Recharge pits and trenches are simple yet effective structures that improve water infiltration.
-
Recharge trenches are filled with gravel or sand to help water move into the soil
-
Recharge pits are ideal for clay-heavy areas where slow percolation is needed
These systems work well in both rural and urban settings.
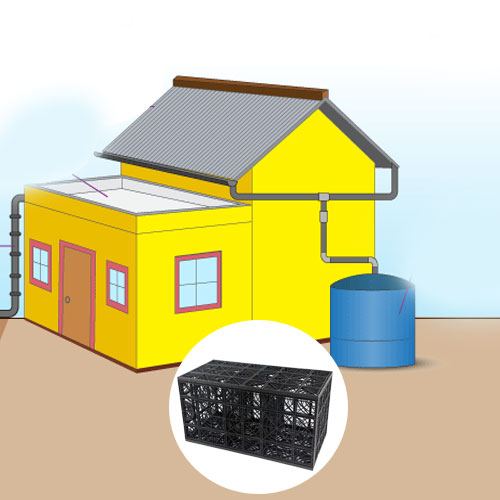
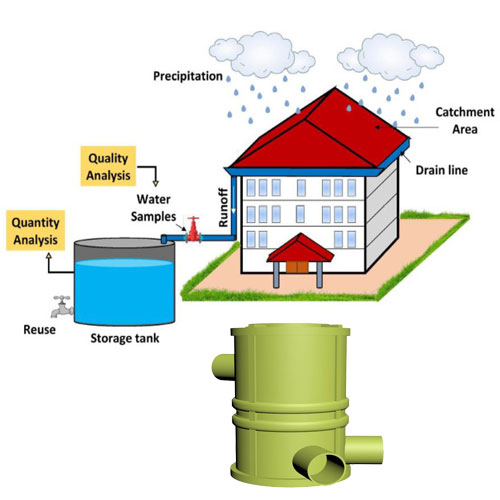
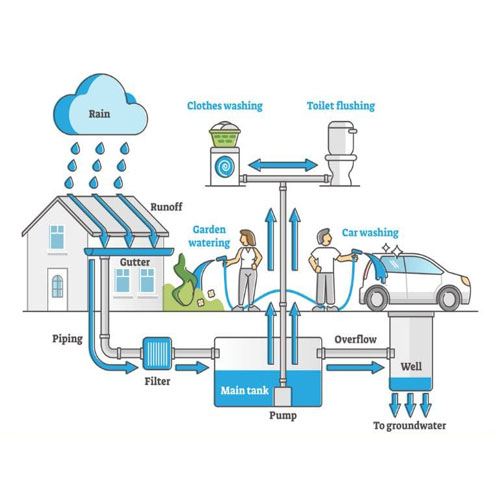
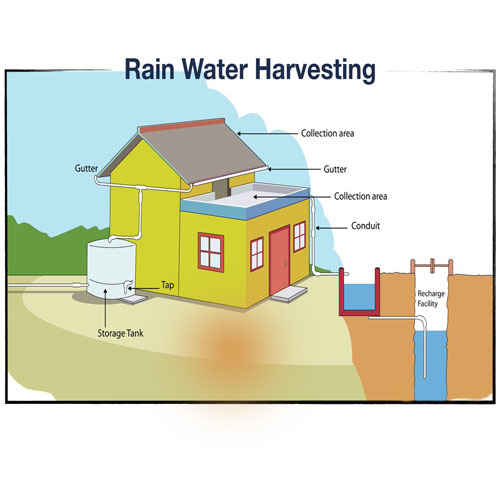
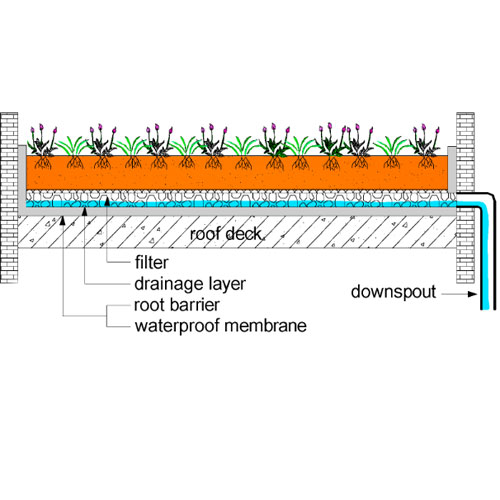
Rooftop Rainwater & Ground Water Recharge System
One of the most effective methods is connecting rooftop rainwater harvesting to recharge structures. Rainwater collected from roofs is guided into recharge pits, recharge wells, or underground chambers.
This approach:
-
Maximizes rainwater use at the source
-
Reduces pressure on drainage systems
-
Promotes localized groundwater recharge
It is a simple yet powerful Ground Water Recharge System.
Ground Water Recharge System Service Provider in Delhi
Implementing a recharge system correctly is just as important as choosing the right method. A professional Ground Water Recharge System Service Provider understands local groundwater conditions, soil types, and government guidelines.
From site assessment and system design to installation and maintenance, an experienced service provider ensures long-term performance and compliance.
Community Awareness & Policy Support Matter
Technology alone is not enough. Public awareness, community participation, and policy support play a major role in the success of any Ground Water Recharge System.
When individuals, housing societies, businesses, and governments work together, groundwater recharge becomes a shared responsibility rather than a forced solution.
A Sustainable Path Forward
A Ground Water Recharge System is more than infrastructure, it is a commitment to future water security. With the right planning and a trusted Ground Water Recharge System Service Provider in Delhi, cities can rebuild their groundwater reserves and reduce long-term water stress.
Rainwater is limited. Recharging groundwater is how we protect it, today and tomorrow.